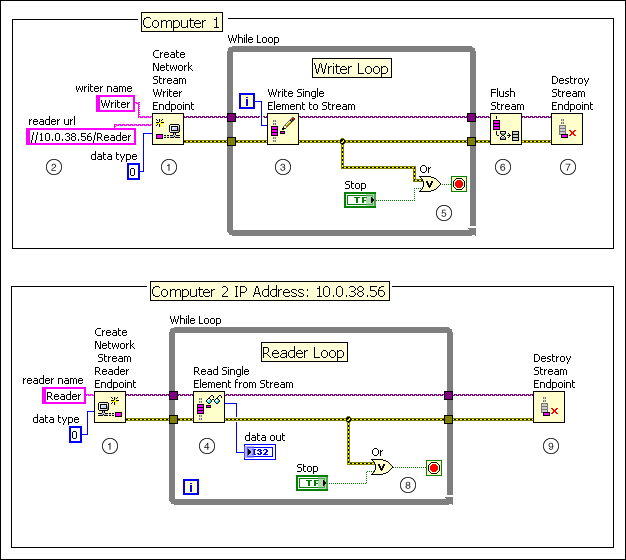
The following figure shows an example of using the Network Streams functions to stream data between two applications on different computers.
The following events occur in the previous figure.
 |
The Create Network Stream Writer Endpoint function creates a writer endpoint on Computer 1, and the Create Network Stream Reader Endpoint function creates a reader endpoint on Computer 2.
 |
Note��You can run the Create Network Stream Writer Endpoint and Create Network Stream Reader Endpoint functions in any order. These functions will create a network stream unless the timeout in ms terminal on one function expires before the other function runs. |
|
 |
The writer endpoint establishes a connection with the reader endpoint using the endpoint URL of the reader endpoint. |
 |
Within the Writer Loop, the Write Single Element to Stream function continuously writes the value of the iteration (i) terminal of the While Loop to the stream.
 |
Note��You also can use the Write Multiple Elements to Stream function to stream more than one data point at a time. For example, use this function if you need to stream two samples of waveform data every second. |
|
 |
Within the Reader Loop, the Read Single Element from Stream function continuously reads the stream.
 |
Note��You also can use the Read Multiple Elements from Stream function to read a stream. You can use a Read Multiple Elements from Stream function even if you used a Write Single Element to Stream function in the other application, and vice versa. |
|
 |
Data streams continuously until the user clicks the Stop button on Computer 1. |
 |
The Flush Stream function transfers all remaining data to the reader endpoint. |
 |
The Destroy Stream Endpoint function destroys the writer endpoint. |
 |
The reader endpoint receives an error due to disconnection, and data flow exits the While Loop. |
 |
The Destroy Stream Endpoint function destroys the reader endpoint, which destroys the stream. |