 |
number of samples/ch specifies the number of samples per channel to read from the file. -1 specifies all samples.
|
 |
sound file refnum is the reference to the sound file. You generate sound file refnum with the Sound File Open VI.
|
 |
position mode, together with position offset, specifies where the read operation begins. Absolute starts the operation at the beginning of the file plus position offset, so the offset is relative to the beginning of the file. Relative starts the operation at the current location of the file mark plus position offset. The default is Relative.
|
 |
position offset specifies how far from the location specified by position mode to start reading. You express position offset in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality.
|
 |
sound file refnum out is the reference to the sound file originally passed in the sound file refnum parameter.
|
 |
data reads any sound data from the file. For multi-channel sound data, data is an array of waveforms where each element of the array is a single channel.
 |
t0 is the start time for the first sample read. LabVIEW calculates the initial start time using the benchmark time of 12:00 a.m., Friday, January 1, 1904, Universal Time [01-01-1904 00:00:00]. Subsequent reads are offset by
BM + (samples * dt)
where BM is the benchmark, samples is the number of samples already acquired, and dt is the sampling interval.
|
 |
dt is the sampling interval of the wave file data.
|
 |
Y is the sound data. If the array data type is a floating-point numeric, Y ranges from -1.0 to 1.0.
The specified data type determines the range of values for the sound data.
|
|
 |
offset indicates the new location of the file mark relative to the beginning of the file, in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality.
|
 |
end of file? returns TRUE when the VI reaches the end of the file.
|
 |
number of samples/ch specifies the number of samples per channel to read from the file. -1 specifies all samples.
|
 |
sound file refnum is the reference to the sound file. You generate sound file refnum with the Sound File Open VI.
|
 |
position mode, together with position offset, specifies where the read operation begins. Absolute starts the operation at the beginning of the file plus position offset, so the offset is relative to the beginning of the file. Relative starts the operation at the current location of the file mark plus position offset. The default is Relative.
|
 |
position offset specifies how far from the location specified by position mode to start reading. You express position offset in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality.
|
 |
sound file refnum out is the reference to the sound file originally passed in the sound file refnum parameter.
|
 |
data reads any sound data from the file. For multi-channel sound data, data is an array of waveforms where each element of the array is a single channel.
 |
t0 is the start time for the first sample read. LabVIEW calculates the initial start time using the benchmark time of 12:00 a.m., Friday, January 1, 1904, Universal Time [01-01-1904 00:00:00]. Subsequent reads are offset by
BM + (samples * dt)
where BM is the benchmark, samples is the number of samples already acquired, and dt is the sampling interval.
|
 |
dt is the sampling interval of the wave file data.
|
 |
Y is the sound data.
|
|
 |
offset indicates the new location of the file mark relative to the beginning of the file, in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality.
|
 |
end of file? returns TRUE when the VI reaches the end of the file.
|
 |
number of samples/ch specifies the number of samples per channel to read from the file. -1 specifies all samples.
|
 |
sound file refnum is the reference to the sound file. You generate sound file refnum with the Sound File Open VI.
|
 |
position mode, together with position offset, specifies where the read operation begins. Absolute starts the operation at the beginning of the file plus position offset, so the offset is relative to the beginning of the file. Relative starts the operation at the current location of the file mark plus position offset. The default is Relative.
|
 |
position offset specifies how far from the location specified by position mode to start reading. You express position offset in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality.
|
 |
sound file refnum out is the reference to the sound file originally passed in the sound file refnum parameter.
|
 |
data reads any sound data from the file. For multi-channel sound data, data is an array of waveforms where each element of the array is a single channel.
 |
t0 is the start time for the first sample read. LabVIEW calculates the initial start time using the benchmark time of 12:00 a.m., Friday, January 1, 1904, Universal Time [01-01-1904 00:00:00]. Subsequent reads are offset by
BM + (samples * dt)
where BM is the benchmark, samples is the number of samples already acquired, and dt is the sampling interval.
|
 |
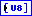
dt is the sampling interval of the wave file data.
|
 |
Y is the sound data. If the array data type is an 8-bit unsigned integer, Y ranges from 0 to 255.
The specified data type determines the range of values for the sound data.
|
|
 |
offset indicates the new location of the file mark relative to the beginning of the file, in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality.
|
 |
end of file? returns TRUE when the VI reaches the end of the file.
|
 |
number of samples/ch specifies the number of samples per channel to read from the file. -1 specifies all samples.
|
 |
sound file refnum is the reference to the sound file. You generate sound file refnum with the Sound File Open VI.
|
 |
position mode, together with position offset, specifies where the read operation begins. Absolute starts the operation at the beginning of the file plus position offset, so the offset is relative to the beginning of the file. Relative starts the operation at the current location of the file mark plus position offset. The default is Relative.
|
 |
position offset specifies how far from the location specified by position mode to start reading. You express position offset in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality.
|
 |
sound file refnum out is the reference to the sound file originally passed in the sound file refnum parameter.
|
 |
data reads any sound data from the file. For multi-channel sound data, data is an array of waveforms where each element of the array is a single channel.
 |
t0 is the start time for the first sample read. LabVIEW calculates the initial start time using the benchmark time of 12:00 a.m., Friday, January 1, 1904, Universal Time [01-01-1904 00:00:00]. Subsequent reads are offset by
BM + (samples * dt)
where BM is the benchmark, samples is the number of samples already acquired, and dt is the sampling interval.
|
 |
dt is the sampling interval of the wave file data.
|
 |
Y is the sound data. If the array data type is a 16-bit signed integer, Y ranges from -32768 to 32767.
The specified data type determines the range of values for the sound data.
|
|
 |
offset indicates the new location of the file mark relative to the beginning of the file, in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality.
|
 |
end of file? returns TRUE when the VI reaches the end of the file.
|
 |
number of samples/ch specifies the number of samples per channel to read from the file. -1 specifies all samples.
|
 |
sound file refnum is the reference to the sound file. You generate sound file refnum with the Sound File Open VI.
|
 |
position mode, together with position offset, specifies where the read operation begins. Absolute starts the operation at the beginning of the file plus position offset, so the offset is relative to the beginning of the file. Relative starts the operation at the current location of the file mark plus position offset. The default is Relative.
|
 |
position offset specifies how far from the location specified by position mode to start reading. You express position offset in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality.
|
 |
sound file refnum out is the reference to the sound file originally passed in the sound file refnum parameter.
|
 |
data reads any sound data from the file. For multi-channel sound data, data is an array of waveforms where each element of the array is a single channel.
 |
t0 is the start time for the first sample read. LabVIEW calculates the initial start time using the benchmark time of 12:00 a.m., Friday, January 1, 1904, Universal Time [01-01-1904 00:00:00]. Subsequent reads are offset by
BM + (samples * dt)
where BM is the benchmark, samples is the number of samples already acquired, and dt is the sampling interval.
|
 |
dt is the sampling interval of the wave file data.
|
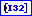 |
Y is the sound data. If the array data type is a 32-bit signed integer, Y ranges from -2147483648 to 2147483647.
The specified data type determines the range of values for the sound data.
|
|
 |
offset indicates the new location of the file mark relative to the beginning of the file, in units of samples. The default is 0.
|
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality.
|
 |
end of file? returns TRUE when the VI reaches the end of the file.
|
 Add to the block diagram
Add to the block diagram Find on the palette
Find on the palette.gif)











.gif)

.gif)

.gif)

.gif)

