Correlation Coefficient VI
Owning Palette: Probability & Statistics VIs
Requires: Full Development System
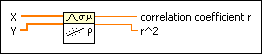
Computes the linear correlation coefficient between input sequences X and Y.
 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |
Owning Palette: Probability & Statistics VIs
Requires: Full Development System
Computes the linear correlation coefficient between input sequences X and Y.

 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |
 |
X is the first input sequence. |
 |
Y is the second input sequence. |
 |
correlation coefficient r returns the correlation coefficient between X and Y. |
 |
r^2 returns the square of correlation coefficient r. |
The linear correlation coefficient also is known as the product-moment coefficient of correlation or Pearson's correlation. The following equation describes the linear correlation coefficient:
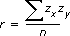
where zx and zy are the standardized z-values of X and Y. The standardized z-values indicate how many standard deviations X and Y are above or below the mean.
correlation coefficient r always is in the interval [–1, 1]. If correlation coefficient r is 1, X and Y have a complete positive correlation. In other words, the data points from X and Y lie on a perfectly straight, positively-sloped line. If correlation coefficient r is –1, X and Y have a complete negative correlation. In other words, the data points from X and Y lie on a perfectly straight, negatively-sloped line. If correlation coefficient r is 0, X and Y have no correlation.