 |
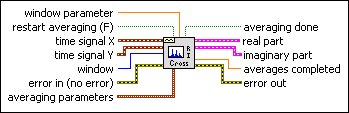
window parameter specifies the beta parameter for a Kaiser window, the standard deviation for a Gaussian window, and the ratio, s, of the main lobe to the side lobe for a Dolph-Chebyshev window. If window is any other window, this VI ignores this input.
The default value of window parameter is NaN, which sets beta to 0 for a Kaiser window, the standard deviation to 0.2 for a Gaussian window, and s to 60 for a Dolph-Chebyshev window.
|
 |
restart averaging specifies whether the VI restarts the selected averaging process. If restart averaging is TRUE, the VI restarts the selected averaging process. If restart averaging is FALSE, the VI does not restart the selected averaging process. The default is FALSE. When you call this VI for the first time, the averaging process restarts automatically. A typical case when you should restart averaging is when a major input change occurs in the middle of the averaging process.
|
 |
time signal X is the time waveform X.
|
 |
time signal Y is the time waveform Y.
|
 |
window (Hanning) is the time-domain window to apply to the time signal. The default window is Hanning.
| 0 | Rectangle | | 1 | Hanning (default) | | 2 | Hamming | | 3 | Blackman-Harris | | 4 | Exact Blackman | | 5 | Blackman | | 6 | Flat Top | | 7 | 4 Term B-Harris | | 8 | 7 Term B-Harris | | 9 | Low Sidelobe | | 11 | Blackman Nutall | | 30 | Triangle | | 31 | Bartlett-Hanning | | 32 | Bohman | | 33 | Parzen | | 34 | Welch | | 60 | Kaiser | | 61 | Dolph-Chebyshev | | 62 | Gaussian |
|
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality.
|
 |
averaging parameters defines how the averaging is computed. The specifications of the parameters include the type of averaging, the type of weighting, and the number of averages.
 |
averaging mode specifies the averaging mode.
| 0 | No averaging (default) | | 1 | Vector averaging | | 2 | RMS averaging | | 3 | Peak hold |
|
 |
weighting mode specifies the weighting mode for RMS and vector averaging.
| 0 | Linear | | 1 | Exponential (default) |
|
 |
number of averages specifies the number of averages used for RMS and vector averaging. If weighting mode is exponential, the averaging process is continuous. If weighting mode is linear, the averaging process stops after this VI computes the selected number of averages.
|
|
 |
averaging done returns TRUE when averages completed is greater than or equal to the number of averages specified in averaging parameters. Otherwise, averaging done returns FALSE. averaging done is always TRUE if the selected averaging mode is No averaging.
|
 |
real part returns the real part of the averaged cross power spectrum and the frequency scale.
 |
f0 returns the start frequency, in hertz, of the spectrum.
|
 |
df returns the frequency resolution, in hertz, of the spectrum.
|
 |
real part is the real part of the averaged cross power spectrum.
|
|
 |
imaginary part returns the imaginary part of the averaged cross power spectrum and the frequency scale.
 |
f0 returns the start frequency, in hertz, of the spectrum.
|
 |
df returns the frequency resolution, in hertz, of the spectrum.
|
 |
imaginary part is the imaginary part of the averaged cross power spectrum.
|
|
 |
averages completed returns the number of averages completed by the VI at that time.
|
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality.
|
 |
weighting mode specifies the weighting mode for RMS and vector averaging.
| 0 | Linear | | 1 | Exponential (default) |
|
 Add to the block diagram
Add to the block diagram Find on the palette
Find on the palette










