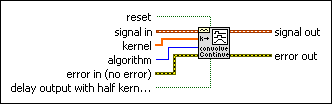
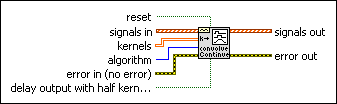
Continuous Convolution (FIR) VI
Owning Palette: Waveform Conditioning VIs
Requires: Full Development System
Convolves single or multiple waveforms and one or more kernels with state, allowing subsequent calls to be processed in a continuous manner. If you are convolving multiple waveforms, the VI maintains separate convolution states for each waveform.
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |