|
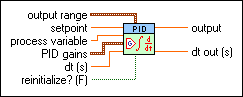
sp low specifies the lower bound of the setpoint range in terms of percentage points or engineering units.
|
 |
sp high specifies the upper bound of the setpoint range in terms of percentage points or engineering units.
|
 |
out low specifies the lower bound of the output range in terms of percentage points or engineering units.
|
 |
out high specifies the upper bound of the output range in terms of percentage points or engineering units.
|
 |
hold specifies whether the controller ignores changes in the process variable and suspends any integral action. If you set hold as TRUE, output will retain its previous value. The default is FALSE.
|
 |
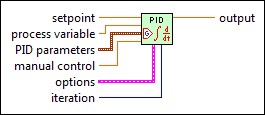
auto? specifies whether to use automatic or manual control. When auto? is�TRUE, this VI uses automatic control. When auto? is FALSE, this VI uses manual control. This VI uses bumpless transfer from manual control to automatic control. The default is TRUE.
This VI resizes the auto? input array to match the size of the process variable input array.
|
 |
pro. band indicates whether the proportional value of PID parameters input is proportional gain (Kc) or proportional band (PB). The default is FALSE, which means the proportional value is proportional gain. The conversion rate is Kc = 100/PB.
|
 |
reverse acting specifies whether the control is reverse- or forward-acting. The default is TRUE, which means output decreases if the input is greater than the setpoint.
|
 |
beta specifies the relative emphasis of setpoint tracking to disturbance rejection. The default value of 1 is appropriate for most applications. You can use a smaller value between 0 and 1 to specify emphasis on disturbance rejection, such as process load changes. The VI uses this value in the two degree-of-freedom algorithm.
|
 |
linearity specifies the linearity of the error response. The valid range for linearity is 0 to 1. A value of 1 provides a normal linear response, while a value of 0.1 provides an approximately parabolic response. The VI uses this value in the nonlinear error calculation and the nonlinear gain factor calculation.
|
 |
dt (s) specifies the loop-cycle time, or interval in seconds, at which this VI is called. If dt (s) is less than or equal to zero, this VI calculates the time since it was last called using an internal timer with 1 ms resolution. If dt (s) must be less than 1 ms, specify the value explicitly. The default is -1.
|
 Add to the block diagram
Add to the block diagram Find on the palette
Find on the palette