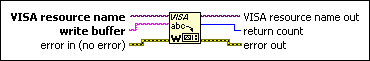
VISA Write Function
Owning Palette: VISA VIs and Functions
Requires: Base Development System
Writes the data from write buffer to the device or interface specified by VISA resource name.
 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |
Owning Palette: VISA VIs and Functions
Requires: Base Development System
Writes the data from write buffer to the device or interface specified by VISA resource name.

 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |
 |
VISA resource name specifies the resource to be opened. The VISA resource name control also specifies the session and class. |
 |
write buffer contains the data to be written to the device. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
VISA resource name out is a copy of the VISA resource name that VISA functions return. |
 |
return count contains the actual number of bytes written. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
Whether the data is transferred synchronously or asynchronously is platform-dependent. Right-click the node and select Synchronous I/O Mode»Synchronous from the shortcut menu to write data synchronously.
When you transfer data from or to a hardware driver synchronously, the calling thread is locked for the duration of the data transfer. Depending on the speed of the transfer, this can hinder other processes that require the calling thread. However, if an application requires that the data transfer as quickly as possible, performing the operation synchronously dedicates the calling thread exclusively to this operation.
 | Note In most applications, synchronous calls are slightly faster when you are communicating with four or fewer instruments. Asynchronous operations result in a significantly faster application when you are communicating with five or more instruments. The LabVIEW default is asynchronous I/O. |
Refer to the following VIs for examples of using the VISA Write function: