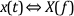The most common applications of the Fourier transform are the analysis of linear time-invariant systems and spectral analysis.
The following equation defines the two-sided Fourier transform.
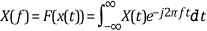
The following equation defines the two-sided inverse Fourier transform.
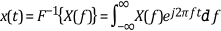
Two-sided means that the mathematical implementation of the forward and inverse Fourier transform considers all negative and positive frequencies and time of the signal. Single-sided means that the mathematical implementation of the transforms considers only the positive frequencies and time history of the signal.
A Fourier transform pair consists of the signal representation in both the time and frequency domain. The following relationship commonly denotes a Fourier transform pair.