Cosine Tapered Window VI
Owning Palette: Windows VIs
Requires: Full Development System
Applies a cosine tapered window to the input sequence X. Wire data to the X input to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |
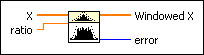




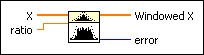


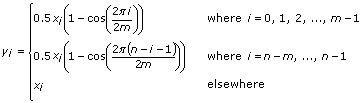
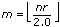 ,
,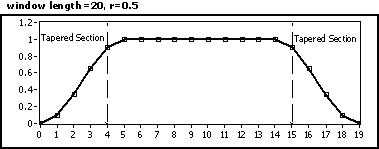
 0, the window is equivalent to a rectangular window. If r
0, the window is equivalent to a rectangular window. If r  1, the window is equivalent to a Hanning window.
1, the window is equivalent to a Hanning window.