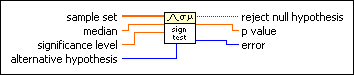
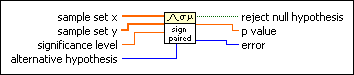
Sign Test VI
Owning Palette: Hypothesis Testing VIs
Requires: Full Development System
Tests hypotheses about the median of continuous distributions. You must manually select the polymorphic instance to use.
As in all hypothesis tests, the hypotheses are statements about the population, not about the sample set. The sign test is a nonparametric test that makes no assumption about the distribution of the underlying population.
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |