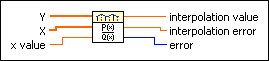
Rational Interpolation VI
Owning Palette: Interpolation & Extrapolation VIs
Requires: Full Development System
Interpolates or extrapolates f at x value using a rational function. The rational function passes through all the points formed by Y and X.
 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |




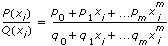
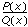
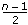 . If the number of points is even, the degrees of freedom of P are
. If the number of points is even, the degrees of freedom of P are 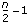 , and the degrees of freedom of Q are
, and the degrees of freedom of Q are 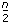 , where n is the total number of points formed by Y and X.
, where n is the total number of points formed by Y and X.