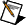Continuous Random VI
Owning Palette: Probability VIs
Requires: Full Development System
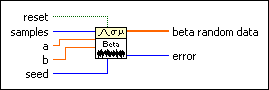
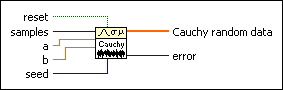
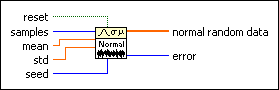
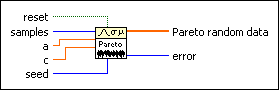
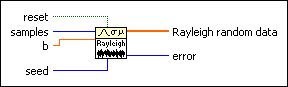
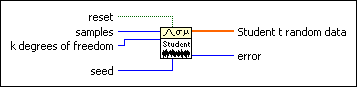
Generates random values from a variate X, where X describes the selected distribution type. You must manually select the polymorphic instance to use.
Use the pull-down menu to select an instance of this VI.
 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |