Sine & Cosine Function
Owning Palette: Trigonometric Functions
Requires: Base Development System
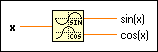
Computes both the sine and cosine of x, where x is in radians. Use this function only when you need both results.
The connector pane displays the default data types for this polymorphic function.
 Add to the block diagram Add to the block diagram |
 Find on the palette Find on the palette |


